區域供冷
As global temperatures continue to rise and the demand for cooling energy increases, we must seek cleaner solutions to cool our buildings and cities. District cooling is a promising option to harness free cooling from sea water and air. It can efficiently cool entire communities from a centralized chiller plant and provide free cooling to large geographical areas. By eliminating the need for individual chillers in every building, district cooling can significantly reduce environmental impact.
Why Alfa Laval in district cooling?
- Alfa Laval has been a pioneering force in plate heat exchangers for almost a century, leading the industry in innovation and sustainability.
- We recognize the growing importance of district cooling and have developed solutions specifically tailored to your needs.
- Our heat exchangers excel in district cooling, saving costs, enhancing energy efficiency, and providing superior cooling performance.
- With a global network of service centres and AHRI certification, you can count on us to provide dependable and flexible heat transfer solutions.
Trend in Industry
The cooling industry is subject to various trends. Without improving energy efficiency, space cooling energy demand is projected to more than triple by 2050, consuming a tremendous amount of electricity. Factors driving the market include growing comfort demand, population growth, decarbonization goals, effective centralized cooling systems, energy costs, and energy-efficient performance.
Some of the trends in the district cooling sector are:
- Cities are implementing more district cooling grids to meet their cooling needs sustainably.
- Rising summer temperatures in traditionally "cold countries" like the Nordics are increasing the demand for cooling.
- The shift from local chiller plants to distributed cooling grids is improving efficiency.
- Microgrids, like those surrounding shopping malls, are becoming popular starting points for larger district cooling grids.
- Global electricity scarcity is driving the adoption of free and centralized cooling in district cooling grids.

Keeping The Louvre and Mona Lisa cold
Over the years, Alfa Laval has become a true partner and has contributed, thanks to its expertise and technology, to the performance of the Climespace energy network, which is the first district cooling system in Europe and one of the biggest in the world."
Jean Levezac, Head of Cluster Connections/Substations at Climespace Engineering
The benefits of district cooling
District cooling presents a sustainable and eco-friendly solution for commercial cooling needs. By centralizing cooling services, it optimizes energy use while eliminating the need for individual electrical chillers in buildings. This not only reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions but also offers financial benefits.
With space-saving advantages and the elimination of costs associated with individual chillers, district cooling proves to be a cost-effective option. The growing global demand for this technology has prompted the industry to explore advanced heat exchanger solutions, enabling increased capacity without requiring additional infrastructure investment.

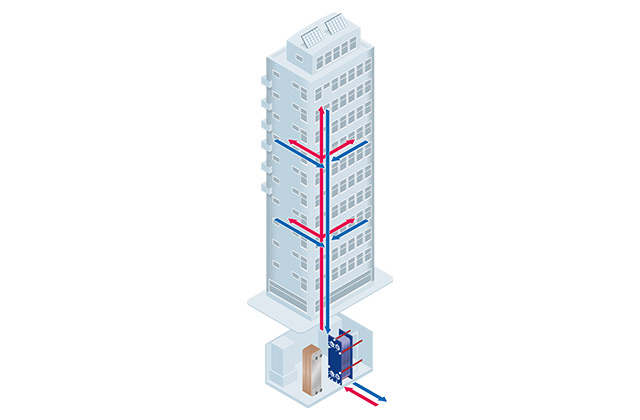
How district cooling works
District cooling efficiently distributes cooling water to buildings using heat exchanger technology from a centralized substation. The heat exchangers have two main purposes: optimizing energy usage by customizing water distribution based on specific building needs and acting as pressure-breakers to control potential damage in case of leaks.
The substation consists of a control unit, control valve, and heat exchangers. The control valve regulates water flow, while the heat exchangers modulate the temperature and capacity for each building. An energy meter measures flow rate and temperature, enabling the calculation of water consumption and final billing.
District cooling integrates energy from multiple locations, reducing stress on electricity demands, incorporating cleaner and free cooling sources, and contributing to net-zero emissions goals.
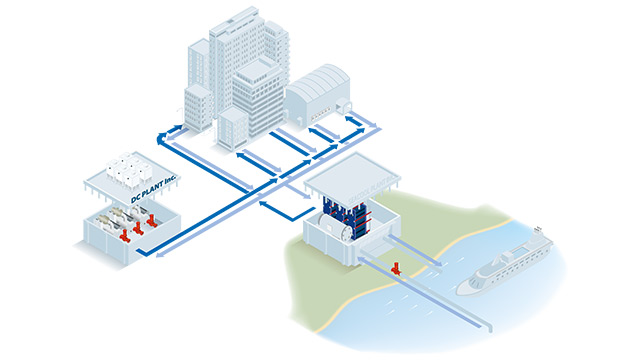
Free cooling from river or sea water
Utilizing sea and river water for free cooling significantly reduces energy consumption, with electricity only needed during extraction. This approach has a high Coefficient of Performance (COP), leading to substantial energy savings compared to traditional chillers. It also reduces the use of harmful refrigerants and fossil fuels, making it an environmentally friendly alternative.
Alfa Laval's plate heat exchanger technology is the ideal solution for safely utilizing various water sources, such as sea, brackish, river, or well water, for free cooling applications. This technology isolates the chilled water loop from sensitive equipment, eliminating the potential for corrosion, scaling, or unwarranted maintenance, ensuring reliable and consistent operation. The compact design of our plate heat exchangers offers space-saving benefits, allowing for much more efficient cooling with minimal fuss.
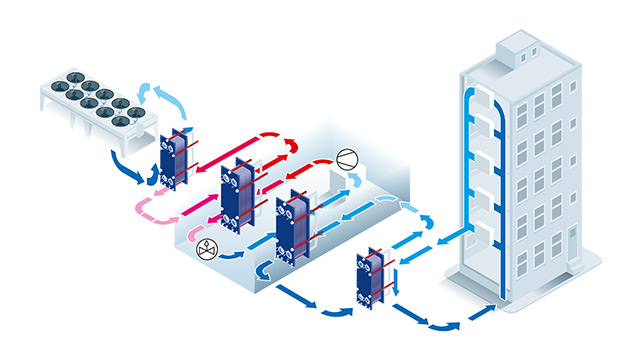
Excess heat in chiller plants can save money and decrease carbon footprint
A chiller plant's primary function is to produce cold, but it also generates excess heat as a by-product. Traditionally, this excess heat is dissipated through cooling towers and air coolers to regulate the plant's temperature. However, reusing this excess heat can be a highly beneficial solution for space heating and domestic hot water.
By recycling the excess heat generated by your chiller plant, you can reduce your reliance on fossil fuels and energy bills while decreasing your carbon footprint.
Absorption chiller – produce efficient cooling from heat
In settings where district heating and excess heat are released at elevated temperatures, a heat-driven absorption chiller can provide efficient cooling. With this approach, you can enjoy the advantages of free cooling without depending on water as your cooling source. Essentially, you can reduce both your electricity usage and the amount of conventional refrigerants required by utilizing the excess heat generated by your production processes.
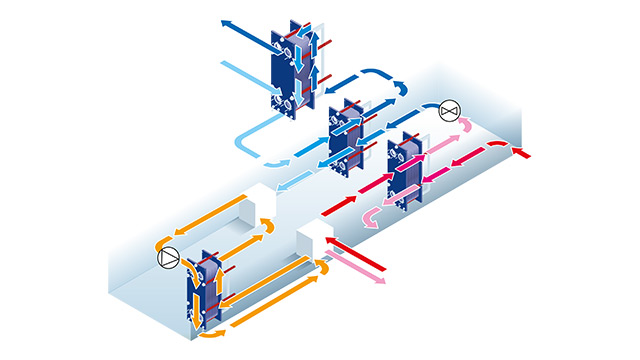
How an absorption chiller works
Within the evaporator, the refrigerant, typically water, absorbs heat from the connected system, causing the air conditioning circuit to cool via a heat exchanger. Afterward, the refrigerant enters the absorber in the form of low-pressure vapor, which is absorbed by a liquid solvent, usually lithium bromide.
A pump increases the pressure of the refrigerant, and the solvent mixture proceeds to an interchanger, where it is preheated, often using a plate heat exchanger. The resulting high-pressure vapor is then directed to the condenser, where heat is released during the refrigerant's condensation process.
半焊可拆板式熱交換器
- 高效可靠的技術,適用於各種因壓力或temperature fatigue而困擾的應用
- 獨特的Alfa Laval RefTight™密封系統,保證更長的生命週期
- 防止介質間的交叉污染,可靠的解決方案
顧問?系統整合商?
顧問們請不要錯過,憑藉在熱交換業界數十年的經驗,阿法拉伐為當今的供暖和降溫挑戰提供了豐富的知識底蘊。您可以在阿法拉伐找到關於能源效率以及天然冷媒等方面的複雜問題的解答,幫助您更輕鬆地找到適合應用的技術工具。

AHRI認證的熱交換器,確保可靠熱性能
我們取得全球對熱性能的AHRI(空氣調節、暖氣和冷凍協會)第三方驗證的認證,為您提供獨立保證,確保板式熱交換器將按照製造商公布的性能指標執行。阿法拉伐提供經過AHRI認證的墊片式板式熱交換器、銅焊式板式熱交換器和擴散焊全不鏽鋼板式熱交換器。

設備效能,歷久彌新
效能不佳的熱交換器,將對現場安全、產品品質和能源成本有負面影響。設備故障可能會導致代價高昂的非預期性停機和重大的生產損失。藉由定期檢測和主動維修保養,讓您可安心使用設備,輕鬆掌握運轉狀況。

數位化提升能源效益
智慧城市和數位智商有助於城市實現70%的永續發展目標。數位服務已經對城市的供暖和降溫系統帶來了顯著影響,向永續邁出一步。
啟用遠程監控並執行專用分析可實現更精確高效的營運、更明智的決策以及更有針對性的干預措施。唯有通過數位轉型才能發展更複雜高效的供暖和冷卻系統,可以為城市區域提供可靠且可負擔的供暖和降溫服務,同時一併減少溫室氣體排放。


