地熱供暖
Geothermal energy can come in different shapes; deep or shallow, high or lower temperature and be used for electricity or heat generation - but have always in common that it is available 24/7. Because it comes from the earth’s crust it is a renewable source that is not dependent on weather or season. Apart from heating, an aquifer storage system can also be used to deliver free cooling to a building.
Choose the right Geothermal Energy partner
- At Alfa Laval, we see the great potential in geothermal energy being an important sustainable heating resource for the future.
- Our goal is to supply energy efficient and reliable solutions that facilitate the highest possible yield at the lowest cost to the environment.
- With nearly 100 years of heat transfer experience and service centers all over the world, We have experience and local presence in all the markets.
- We know which heat exchanger will best optimize your production with the lowest possible payback time.
- With AHRI third party performance certification, you can rest easy that the thermal performance of our products is as good as we say it is.
Trends in geothermal heating industry
Focus on geothermal energy as an alternative to traditional fossil fuels is on the rise in the heating sector. Especially where it can replace fuels in district heating networks and reach a large number of customers from one single set of wells. There is also a growing experience for use of shallow geothermal with lower available temperature and aquifer thermal storage systems together with heat pumps to form a affordable and energy efficient options on the renewable energy market.
However, this industry doesn’t come without challenges. As the water can contain high levels of chloride and other impurities, scaling and fouling can build up and reduce the performance of process equipment. That is where we come in. Alfa Laval’s high-quality equipment and experience in the field of service are proven to keep your processes at optimum capacity with minimal downtime.

When it comes to equipment, we simply have to pick the best. The supplier must be able to prove a powerful capacity for after sales services and emergency preparedness. We are happy to say, that Alfa Laval fulfils these uncompromising criteria with a very safe margin.
Ali Ichedef, General Manager of Izmir Jeotermal
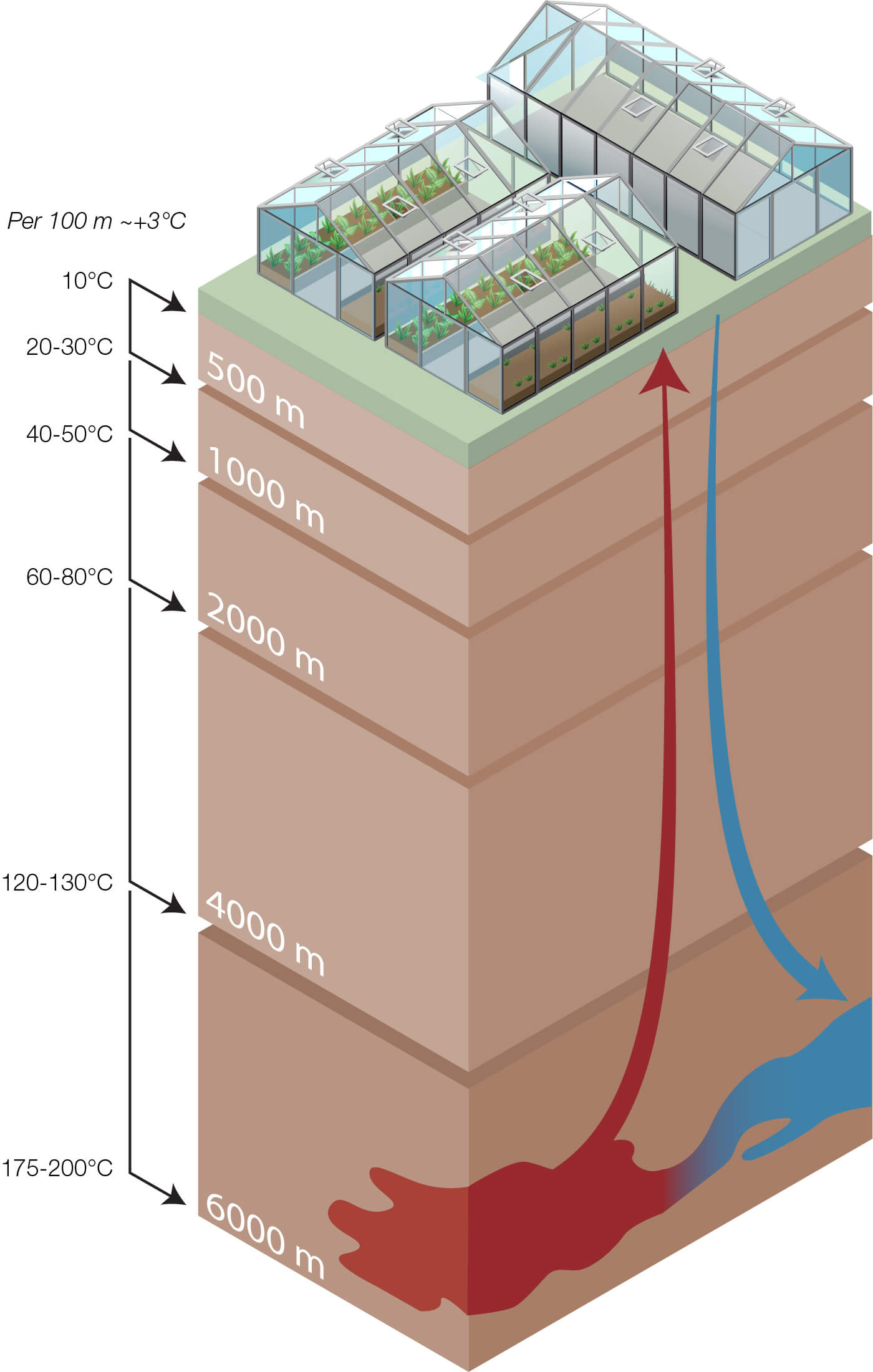
The Geothermal temperature gradient depends on the depth of the well together with the location. Some locations can have higher temperatures close to surface level, for example, Iceland. However, most locations have a temperature range illustrated by the graph.
Geothermal heating works by extracting the heat from an underground water source. The further underground the water is extracted, the hotter it usually is. In the Netherlands, geothermal heat plants pump warm water from depths of at least 500 meters. When heat has been drawn from the geothermal water it is returned to the ground in the injection well.
The Netherlands is the world’s second-largest food exporter by value, and the country’s 9000 hectares of greenhouses are a big reason why. But keeping those greenhouses at the right temperature requires lots of energy, so developing alternative energy sources is a top priority in the country’s efforts to meet its ambitious climate targets.
Heat exchangers play a key role in harnessing the benefits to geothermal energy, ensuring efficient heat transfer between the warm water coming up from the ground and the cooler water that has been used to heat greenhouses or other buildings.
Difference between shallow, aquifer and deep geothermal
Every well is unique with depths changing depending on location and conditions. When this industry talks about shallow or deep wells it is really to identify the main characteristics of a project. Shallow geothermal heat is generated from subsurface water using either an open loop where water is pumped from the well or a closed loop system with brine in a collector loop which is pumped up and down in the well.
Shallow wells and aquifers (<=500m)
Shallow geothermal heating, and ATES (aquifer thermal energy storage) is a renewable energy technology that uses the relatively constant temperature of the upper layers of the earth's crust to heat and/or cool buildings.
Unlike deep geothermal systems, shallow geothermal systems typically operate at depths of up to 100 meters.
Shallow geothermal wells generate a temperature level that cannot be used directly as it is – hence the absorbed heat in a shallow geothermal project is used together with heat pumps, which increases the temperature to a more useful temperature level for heating purposes. A shallow geothermal system can also be used in reverse where the water below ground is used as a free cooling source to cool buildings during hot weather.
Shallow geothermal systems are a popular choice for residential and small commercial buildings, as they can be installed in a relatively small space and require less drilling and excavation than deep geothermal systems.
Deep wells (2000 - 5000m)
Deep geothermal heating, is a renewable energy source that uses the heat which comes from the core of the earth.
The hot water and potentially even steam are brought to the surface and used to generate heat by running it through a heat exchanger where energy is transferred to the second level where it is distributed to the point where it is being used. From deed geothermal wells the temperature can be high enough to be used directly as it is. But at some locations and depths, there can still be a need for increasing the temperature level with heat pumps. It is quite common that deep geothermal sources are connected to a district heating system.
The depth at which deep geothermal systems operate can vary depending on several factors, including the geological characteristics of the area, the type of system being used, and the heat requirements of the buildings in which the heat is being used.
In general, deep geothermal systems operate at depths ranging from about five hundred meters to several kilometers below the surface. The most common depths for deep geothermal systems used for delivering heating to buildings and greenhouses are between 1,500 and 3,000 meters.
半焊可拆板式熱交換器
- 高效可靠的技術,適用於各種因壓力或temperature fatigue而困擾的應用
- 獨特的Alfa Laval RefTight™密封系統,保證更長的生命週期
- 防止介質間的交叉污染,可靠的解決方案
AHRI認證的熱交換器,確保可靠熱性能
我們取得全球對熱性能的AHRI(空氣調節、暖氣和冷凍協會)第三方驗證的認證,為您提供獨立保證,確保板式熱交換器將按照製造商公布的性能指標執行。阿法拉伐提供經過AHRI認證的墊片式板式熱交換器、銅焊式板式熱交換器和擴散焊全不鏽鋼板式熱交換器。

顧問?系統整合商?
顧問們請不要錯過,憑藉在熱交換業界數十年的經驗,阿法拉伐為當今的供暖和降溫挑戰提供了豐富的知識底蘊。您可以在阿法拉伐找到關於能源效率以及天然冷媒等方面的複雜問題的解答,幫助您更輕鬆地找到適合應用的技術工具。

設備效能,歷久彌新
效能不佳的熱交換器,將對現場安全、產品品質和能源成本有負面影響。設備故障可能會導致代價高昂的非預期性停機和重大的生產損失。藉由定期檢測和主動維修保養,讓您可安心使用設備,輕鬆掌握運轉狀況。

數位化提升能源效益
智慧城市和數位智商有助於城市實現70%的永續發展目標。數位服務已經對城市的供暖和降溫系統帶來了顯著影響,向永續邁出一步。
啟用遠程監控並執行專用分析可實現更精確高效的營運、更明智的決策以及更有針對性的干預措施。唯有通過數位轉型才能發展更複雜高效的供暖和冷卻系統,可以為城市區域提供可靠且可負擔的供暖和降溫服務,同時一併減少溫室氣體排放。